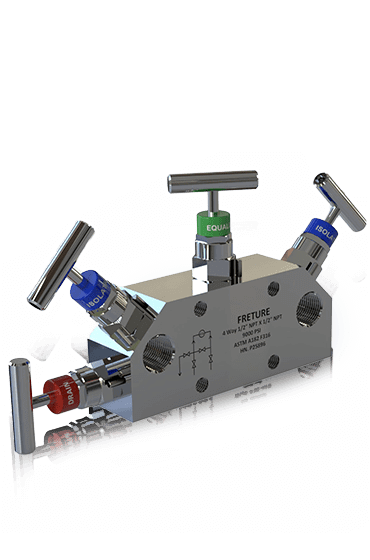
In the realm of industrial instrumentation, the precision and reliability of valve systems play a crucial role in ensuring seamless operations. Among the various types of valves, 4-way manifold valves have emerged as a pivotal component in complex industrial processes. These valves, known for their versatility and efficiency, are designed to manage the flow of fluids and gases in intricate systems. In this article, we delve into the world of 4-way manifold valves, exploring their design, functionality, and applications, and highlighting why they are an essential choice for industries seeking optimal control and performance.
Understanding 4-Way Manifold Valves
A 4-way manifold valve is a sophisticated device engineered to control the flow path of fluids or gases in multiple directions. Unlike traditional valves that offer limited flow control, 4-way manifold valves provide four distinct flow paths, enabling more complex routing of fluids within a system. This design is particularly advantageous in applications where precise control over flow direction is required, such as in hydraulic systems, pneumatic systems, and process control environments.
Key Features and Components
The design of 4-way manifold valves incorporates several key features that contribute to their superior performance:
Multiple Ports: As the name suggests, 4-way manifold valves have four ports, typically labeled as P (Pressure), T (Tank), A (Actuator), and B (Actuator). These ports allow the valve to direct the flow of fluids or gases to different parts of the system.
Balanced Design: Many 4-way manifold valves feature a balanced design, ensuring that the pressure is evenly distributed across the valve. This minimizes wear and tear, enhancing the valve's longevity and reliability.
High-Quality Materials: To withstand harsh industrial environments, 4-way manifold valves are constructed from durable materials such as stainless steel, brass, and other corrosion-resistant alloys. This ensures optimal performance even in challenging conditions.
Precision Engineering: The internal components of 4-way manifold valves are meticulously engineered to provide precise control over flow rates and directions. This precision is crucial for maintaining the integrity of industrial processes.
Functionality and Operation
The primary function of a 4-way manifold valve is to control the direction of fluid flow within a system. This is achieved through the manipulation of the valve's internal components, which can be manually operated or controlled by an actuator. Here’s a breakdown of how these valves operate:
Directional Control: By adjusting the position of the valve, the operator can direct the flow of fluid from the pressure port (P) to either of the actuator ports (A or B), and from the actuator ports to the tank port (T). This allows for versatile flow routing within the system.
Flow Regulation: 4-way manifold valves also provide precise regulation of flow rates, ensuring that the desired amount of fluid reaches each part of the system. This is particularly important in applications where maintaining specific flow rates is critical for process efficiency.
Isolation and Venting: These valves can also isolate sections of the system or vent fluids to prevent overpressure. This feature is essential for safety and maintenance purposes.
Applications of 4-Way Manifold Valves
The versatility and efficiency of 4-way manifold valves make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. Here are some key areas where these valves are commonly used:
Hydraulic Systems: In hydraulic machinery and equipment, 4-way manifold valves control the movement of actuators, ensuring precise positioning and operation. They are integral to the functioning of hydraulic presses, lifts, and other heavy machinery.
Pneumatic Systems: These valves are also used in pneumatic systems to control the flow of compressed air. Applications include air-powered tools, automation systems, and various types of pneumatic machinery.
Process Control: In industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and pharmaceuticals, 4-way manifold valves are used to manage the flow of liquids and gases through complex process pipelines. Their ability to provide precise control over flow rates and directions is crucial for maintaining process integrity.
HVAC Systems: In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, 4-way manifold valves are used to regulate the flow of refrigerants and other fluids. This ensures efficient operation and temperature control within the system.
Advantages of 4-Way Manifold Valves
The adoption of 4-way manifold valves in industrial applications offers several significant advantages:
Enhanced Control: The ability to direct fluid flow in multiple directions provides greater flexibility and control over industrial processes. This can lead to improved efficiency and productivity.
Reduced Complexity: By consolidating multiple flow paths into a single valve, 4-way manifold valves simplify system design and reduce the need for additional components. This can lower installation and maintenance costs.
Improved Safety: The isolation and venting capabilities of these valves enhance system safety by preventing overpressure and allowing for safe maintenance procedures.
Durability and Reliability: Constructed from high-quality materials and designed for balanced operation, 4-way manifold valves offer long-term reliability and reduced downtime.
Freture Techno Pvt. Ltd.: Your Partner in Precision Valves
At Freture Techno Pvt. Ltd., we understand the critical role that precision valves play in industrial operations. Our 4-way manifold valves are designed and manufactured to meet the highest standards of quality and performance. With a commitment to innovation and customer satisfaction, we offer a range of valve solutions tailored to the specific needs of our clients.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial instrumentation, the importance of efficient and reliable valve systems cannot be overstated. 4-way manifold valves stand out as a versatile and effective solution for managing fluid flow in complex systems. Their unique design, coupled with precision engineering and high-quality materials, makes them an invaluable asset in various industrial applications. For industries seeking to enhance control, improve efficiency, and ensure safety, 4-way manifold valves from Freture Techno Pvt. Ltd. are the ideal choice. Embrace the future of industrial valve technology with our innovative solutions, and experience the difference in performance and reliability.
For more information on our range of 4-way manifold valves, visit Freture Techno Pvt. Ltd. today and discover how we can support your industrial needs.